In addition, the Class A AIS unit broadcasts the following information every 6 minutes. Should only be used by Class A shipborne and SAR aircraft AIS stations when reporting static or voyage related data:
|
Parameter |
Bits |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Message ID |
6 |
Identifier for this Message |
|
Repeat indicator |
2 |
Used by the repeater to indicate how many times a message has been repeated. Refer to §?4.6.1, Annex 2; 0-3; 0 = default; 3 = do not repeat any more |
|
User ID |
30 |
MMSI number |
|
AIS version indicator |
2 |
0 = station compliant with Recommendation ITU-R M.1371-1 |
|
IMO number |
30 |
0 = not available = default – Not applicable to SAR aircraft |
|
Call sign |
42 |
7?=?6 bit ASCII characters, @@@@@@@ = not available = default |
|
Name |
120 |
Maximum 20 characters 6 bit ASCII "@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@" = not available = default |
|
8 |
0 = not available or no ship = default |
|
|
30 |
Reference point for reported position. |
|
|
4 |
0 = undefined (default) |
|
|
ETA |
20 |
Estimated time of arrival; MMDDHHMM UTC |
|
Maximum present static draught |
8 |
In 1/10 m, 255 = draught 25.5 m or greater, 0 = not available = default; in accordance with IMO Resolution A.851 |
|
Destination |
120 |
Maximum 20 characters using 6-bit ASCII; |
|
DTE |
1 |
Data terminal equipment (DTE) ready (0 = available, 1 = not available = default) |
|
Spare |
1 |
Spare. Not used. Should be set to zero. Reserved for future use. |
|
Number of bits |
424 |
Occupies 2 slots |
Type of ship
denoted in the USCG AIS Encoding Guide) ***
|
Identifiers To Be Used By Ships To Report Their Type |
|
|
Identifier No. |
Special craft |
|---|---|
|
50 |
Pilot vessel |
|
51 |
Search and rescue vessels |
|
52 |
Tugs |
|
53 |
Port tenders |
|
54 |
Vessels with anti-pollution facilities or equipment |
|
55 |
Law enforcement vessels |
|
56 |
Spare - for assignments to local vessels |
|
57 |
Spare - for assignments to local vessels |
|
58 |
Medical transports (as defined in the 1949 Geneva Conventions and Additional Protocols) |
|
59 |
Ships and aircraft of States not parties to an armed conflict |
|
Identifiers to be used by ships to report their type |
||||
Other ships |
||||
|
First digit(1) |
Second digit(1) |
First digit(1) |
Second digit(1) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 - Reserved for future use |
0 - All ships of this type |
- |
0 - Fishing |
|
|
2 - WIG |
1 - Carrying DG, HS, or MP, IMO hazard or pollutant category X |
- |
1 - Towing |
|
|
3 - See right column |
2 - Carrying DG, HS, or MP, IMO hazard or pollutant category Y |
3 - Vessel |
2 - Towing and length of the tow exceeds 200 m or breadth exceeds 25 m |
|
|
4 - HSC |
3 - Carrying DG, HS, or MP, IMO hazard or pollutant category Z |
- |
3 - Engaged in dredging or underwater operations |
|
|
5 - See above |
|
- |
4 - Engaged in diving operations |
|
|
|
5 - Reserved for future use |
- |
5 - Engaged in military operations |
|
|
6 - Passenger ships |
6 - Reserved for future use |
- |
6 - Sailing |
|
|
7 - Cargo ships |
7 - Reserved for future use |
- |
7 - Pleasure craft |
|
|
8 - Tanker(s) |
8 - Reserved for future use |
- |
8 - Reserved for future use |
|
|
9 - Other types of ship |
9 - No additional information |
- |
9 - Reserved for future use |
|
(1) The identifier should be constructed by selecting the appropriate first and second digits.
The second digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 reflecting categories X, Y, Z and OS formerly were categories A, B, C and D.
Reference point for reported position and overall dimensions of ship
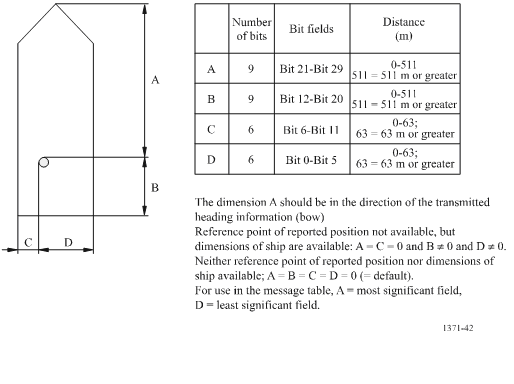
(Source: International Telecommunications Union Recommendation ITU-R M.1371-5)
External Position Fixing System (EPFS)
An EPFS can be any navigation system, receiver or integrated navigation system (INS), having an IEC 61162 interface. On a Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) Convention ship the navigation system must meet IMO performance standards and be certified. In practice, most EPFS systems are currently GPS, and some GPS devices provide a dead reckoning (estimated position) mode. The type of EPFS used is derived from IEC 61162-1 sentence GLL, VTG, GDT, and ROT from the sensor input and is transmitted by the four bit Class A Message 5 or Class B Message 19. It is understood that the overwhelming majority of EPFS sensors interfaced with AIS are GPS. If an EPFS device is not connected to the AIS, the internal AIS GPS is used to provide position. The table describes fallback conditions and priority for how these positions sensors are used by AIS.
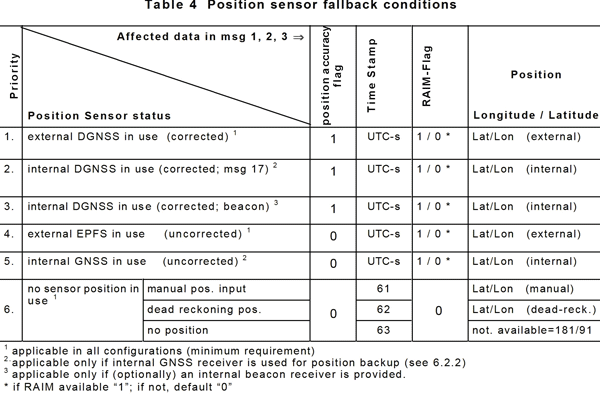
(Source International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 61993-2)